React&Redux로 시작하는 웹프로그래밍_8주차
css in js의 문제점: https://speakerdeck.com/vjeux/react-css-in-js
React라이브러리: styled-components
스타일링 라이브러리 (스타일 관련 컴포넌트)
https://styled-components.com/
*프로젝트 설정하기*
1. 프로젝트 만들기
2. 리액트 설치
3. 스타일드 컴포넌트 설치 (my-app안에 설치하기)
*참고: 프로젝트 컴파일 전에 설치하기
* package.json에서 설치 확인하기4. 폴더설정과 파일만들기
4-1. components 폴더 안에 .jsx파일 만들기
4-2. .jsx파일에 rfc 이후 스타일드 컴포넌트 파일 (getting start 부분 복붙)
import React from 'react'
import styled from 'styled-components'; // styled 연결해주기
export default function StyledComponentExample() {
// Create a Title component that'll render an <h1> tag with some styles
const Title = styled.h1`
font-size: 1.5em;
text-align: center;
color: palevioletred;
`;
// Create a Wrapper component that'll render a <section> tag with some styles
const Wrapper = styled.section`
padding: 4em;
background: papayawhip;
`;
// Use Title and Wrapper like any other React component – except they're styled!
return(
<Wrapper>
<Title>
Hello World!
</Title>
</Wrapper>
);
}
6. 브라우저에서 정상작동하는지 확인하기
* button 예제
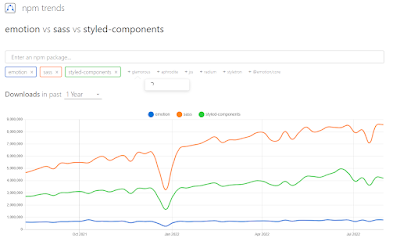
* 라이브러리 트랜드 확인하기
검색: npm trend
주소: https://npmtrends.com/
원하는 라이브러리를 선택해 비교도 가능함
React 라이브러리: Redux
Redux가 하는 일: 스토어를 통해 컴포넌트들이 상태를 업데이트 한다. 상태가 변경되면 자동 랜더링이 된다.
스타일링 라이브러리 (스타일 관련 컴포넌트)
https://styled-components.com/
*프로젝트 설정하기*
1. 프로젝트 만들기 (폴더명 예: redux-start)
2. 리액트 설치
3. Redux 라이브러리 설치 (my-app 안에 설치하기)
4. 개발 서버 열기
5. 액션 만들기
6. 리듀서
리덕스의 리듀서란,
Pure Function (항상 같은 인풋을 받아 항상 같은 리턴을 함) 시간에 따른 변화는 없어야함
리듀서를 통해서 상태가 바뀌었는지 확인한다.
function 리듀서 (previousState, action {
return newState;
}
이뮤터블해야함, 즉 오리지날 스테이트와 새로만들어진 스테이트는 별도에 객체로 만들어져, 두개가 비교되어 상태가달라졌음을 리덕스가 인지함